Intermittent fasting is not so much a diet but a pattern or timing of how to eat. It is how early mankind fed itself for millennia. It has many benefits to improve our health. This article discusses intermittent fasting (IF), types of intermittent fasting and subsequent health benefits.
To be very clear this article is meant for general purposes and should not be utilized individually, but in consultation with one’s health care provider.
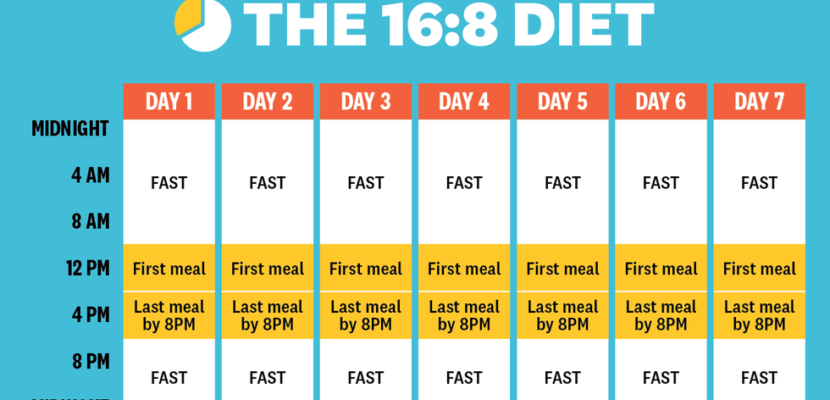
Let’s begin with stating that intermittent fasting means NO SNACKS! Snacking is out. Intermittent means we will wait an interval of time between meals.
There are various patterns that can be used for intermittent fasting. One of the simplest is: 3 square meals a day. This is a time-honored custom for many in the boomer generation and previous generations. It involves having breakfast, lunch and dinner and not eating overnight. Typically, a 4-5 hour time span between meals occurs. Since each meal is substantial the individual doesn’t become hungry.
Another method of IF is to utilize the 3 square meals a day and to add a 24- 48 hour fasting time once a month where one only drinks water and sparingly drinks a vegetable broth.
There are a number of other patterns that can pursue and are readily investigate by consulting an expert of nutrition and online references.
The benefits of IF are numerous, ranging from weight loss, improved metabolism, decreased chronic pain and lower risk of cancer.
Weight loss occurs when we refrain from eating for longer periods. If we eat frequently, we are constantly burning calories from the food we’ve consumed. However, by utilizing IF we burn fat and subsequently lose weight.
Many people feel that their metabolism is slow or unstable. Intermittent fasting can speed up and stabilize overall body metabolism. Physiologically IF reduces the amount of insulin produced by the pancreas and allows blood glucose levels to normalize. Over weeks and months metabolic activities of the body naturally become more balanced, normal and regular.